1. Why are electric cars prone to catching fire?
The essence of a fire is thermal runaway, where a substance reaches its ignition point and happens to have the reactants needed for combustion. There are many reasons for thermal runaway, and the main ones in daily use are: (1) improper charging, excessive voltage and current, severe heating, and explosion; (2) Internal short circuit, explosion: Because the separator in the lithium battery is damaged by external force (such as squeezing, or something is directly inserted, such as metal puncture), the positive and negative poles inside the lithium battery are connected, forming an internal short circuit and quickly discharging. (Actually, electric vehicles entering elevators usually do not ignite spontaneously. If you look at those surveillance videos again, you will find that many times the electric vehicle battery is caught by the elevator door and catches fire.); In this (2), there is also a possibility that the battery is used, and the negative electrode is "long" enough to pass through the separator and directly contact the positive electrode, which can also cause a short circuit. This is called lithium dendrite.
.png)
2.What is an internal short circuit?
Under normal circumstances, there is a potential difference between the positive and negative electrodes, and electrons are affected by the electric field and move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the external circuit (because electrons cannot flow in the electrolyte, they will be captured by various ions and cannot come out, so they can only go outside. As we all know, electricity chooses the route with the lowest resistance). Lithium(Li+) ions inside the lithium battery also flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode through the blue electrolyte, pass through the middle separator, and combine with the electrons in the external circuit to form a more stable Li (actually LiC6, which is Li arranged neatly in graphite, with one lithium wrapped in every six carbons, and has a relatively stable structure). However, if there is a steel wire inside that connects the positive and negative electrodes (or if the positive and negative electrodes directly collide with each other), Because the resistance of the steel wire is extremely small, the current becomes extremely large, generating heat of I ² * R and rapidly heating up. Remark:I=U/R,(I means current,U means voltage (or potential difference) ,R means resistor.
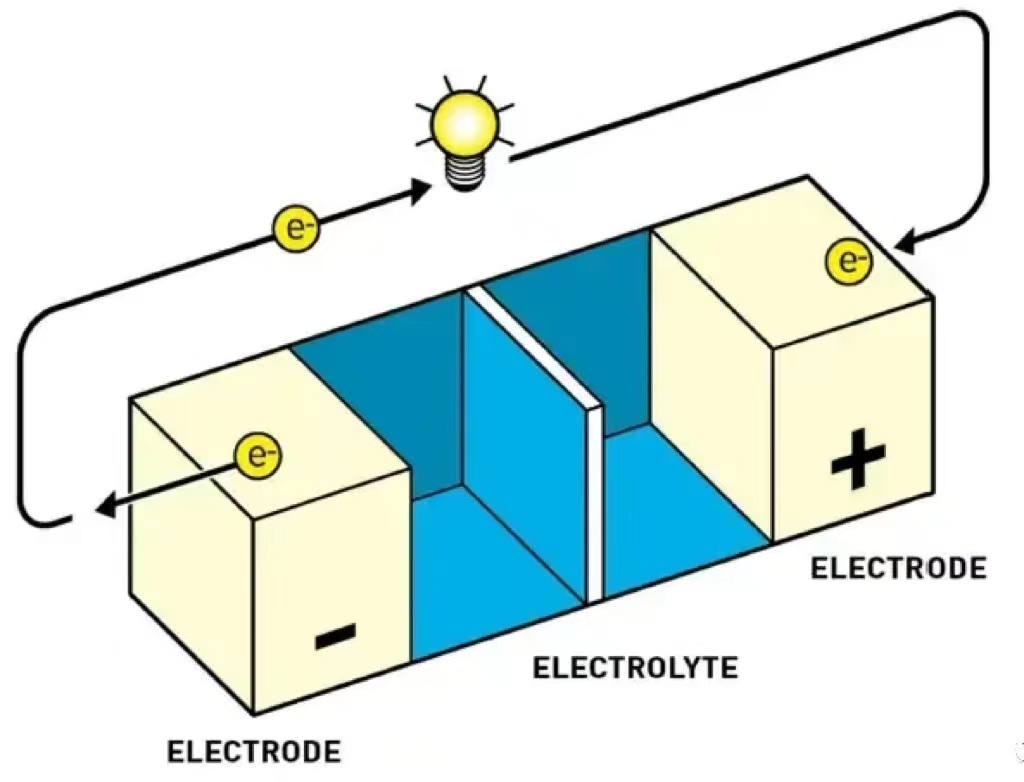
3. Why do the positive and negative electrodes seem to come into contact so easily, and is the separator useless? Lithium batteries have been studied for more than 100 years, why is the strength of the separator still so low?

Although Figure 2 appears to have the positive and negative poles far apart, it is actually like Figure 3, where the material is only a thin layer. This is because, if the distance is far, it would be difficult for lithium ions to pass through (due to high internal resistance and low energy efficiency). Therefore, in order to meet consumers' extreme demands for electric vehicle range and acceleration, manufacturers can only make the positive and negative poles very close, and after rolling, they need to press them again to make them more compact.
However, the Battery diaphragm does not actually participate in the reaction, but only protects the positive and negative electrodes from contact. Therefore, the more holes in the middle separator, the better, and the thinner the better. Therefore, performance and safety are trade-off alternative. Finally, after balancing, polyethylene(PE) and polypropylene(PP),plastic material , the two most common film separator materials nowadays. The film is thin and can be pierced easily by steel after a collision.
Then the lithium dendrite mentioned above refers to the lithium that was originally intended to enter the negative electrode obediently during charging, but it deviated and formed metallic lithium on the surface of the negative electrode, gradually growing through the separator and coming into contact with the positive electrode. Because the diaphragm has holes which cannot prevent this from happening, even with solid electrolytes. Lithium dendrites will extend along small cracks in the middle of the solid.
3. Why does an internal short circuit ignite when it releases heat?
Firstly, we need to understand that material combustion is a rapidly exothermic redox reaction. An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the release of heat during a reaction process. The essence is that the energy absorbed by the breaking of chemical bonds is less than the energy released by the formation of new chemical bonds. As for what a chemical bond itself is, it cannot be fully explained at present. The most mainstream theory in the scientific community is to use quantum mechanics to explain it. In an atom, electrons move around the nucleus, and then bonding is formed because electrons discover that they move around two atoms at the same time, which seems to have lower energy (more stable), so the two atoms are bound together. Breaking this chemical bond requires external input of energy (heat absorption), while forming it (bonding) is a process of moving from a high-energy state to a low-energy state, thus releasing heat. And here the exothermic>endothermic, the overall manifestation is an exothermic reaction.
Combustion can be explained by the simplest reaction equation of hydrogen burning to form water, 2H2+O2=2H2O. The sum of the energy absorbed by H-H bond cleavage and O=O bond cleavage is less than the energy released by H-O-H bonding, so the combustion of hydrogen is exothermic.
But all the stable substances we encounter in our daily lives do not spontaneously ignite at room temperature, just like two H's that were originally fine and didn't look too much at O. However, as the temperature increased, H and O collided and rubbed wildly, causing a dry fire. H realized that O had a greater attraction than the other H and joined together. But these substances will not burn until the temperature reaches their ignition point. The following figure lists the ignition points of different materials in mainstream lithium batteries, generally known as the barrel effect. The one that burns first will ignite the entire battery pack.
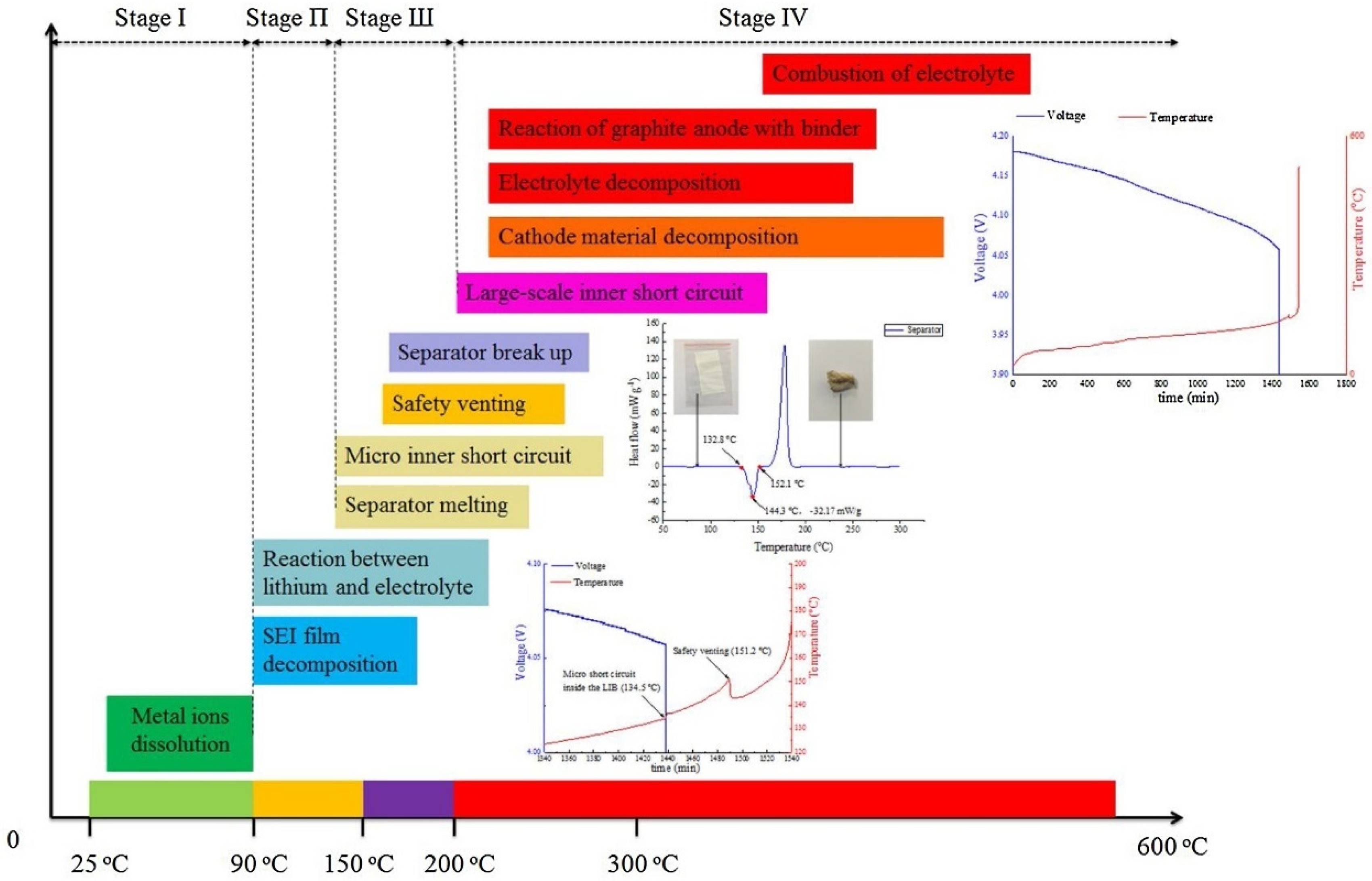
After BYD's blade battery was punctured, it only smoked/caught fire on a small scale, without burning/exploding. This is because its positive electrode is a lithium iron phosphate Before reaching 300 degrees Celsius, the positive electrode was still fine (but after smoking for a long time, it gradually reached this ignition point, and there is also a possibility of fire or even explosion).
5. What is the difference between lithium batteries used in mobile phones and electric vehicles(EV)?
The biggest difference is the power, the amount of electricity that needs to be discharged in an instant is different, so as long as something fails, the danger in the EV will be instantly amplified.Another important difference is the usage environment. A mobile phone in a pocket has a buffer when shaken, and it may not fall to the ground twice a week. However, a car experiences severe vibrations every moment, and any pit on the road may be equivalent to a phone falling many times. It has also been used for a long time, at least five years. In the past, many cars have been used for ten years. After two or three years, even if the mobile phone battery is not bad, it is because the too laggy needs to be replaced, so it is rare to continue to use it when the battery is in poor condition. But for electric cars, unless there is a major malfunction, it is difficult to detect poor battery condition. Therefore, if the battery is injured on the road and accidentally hit again, it may unfortunately explode.
6. Why is it so difficult to extinguish a EV fire?
Because it burns not only with oxygen as a reactant, as shown in Figure 4, the combustion of the negative electrode and electrolyte itself can release a large amount of heat. Therefore, using dry powder to isolate oxygen cannot be flame retardant. It must be continuously sprayed with water to cool down the system before the combustion can be stopped. However, water itself conducts electricity, and the battery system of a car that catches fire is usually damaged. Therefore, if water enters, it will short circuit and ignite, causing a cycle of continuous burning that is difficult to extinguish.
7.Why does improper charging often lead to battery explosions, especially for electric bicycles?
In short, as long as the voltage is too high, it is possible to snatch out the originally inactive electrons in the inner layers of various elements in the battery structure, causing the entire system to collapse. Therefore, as long as the voltage is high enough, any battery can be charged and exploded (Liquid sulfur batteries excluded).
Then all electric vehicles have a BMS (battery management system) power management system, one of which is used to control the cut-off voltage/current of battery charging and discharging to prevent overcharging and overdischarging. However, the BMS of electric bicycles may not be as good, or the circuit may not be as strong, and the direct charging voltage may be so high that it breaks down the protective circuit/isolation chip. So according to the battery instructions and regulations, charge it well and don't try to charge it too quickly. Otherwise, if the voltage is too high, even if it doesn't explode,it will reduce battery lifespan.
Install photovoltaic energy storage systems for your own home or company to save money and stabilize electricity consumption
Find a stable and reliable factory to assist you in expanding the market locally
Professional technical team and reliable energy storage products to provide a guarantee for your engineering project